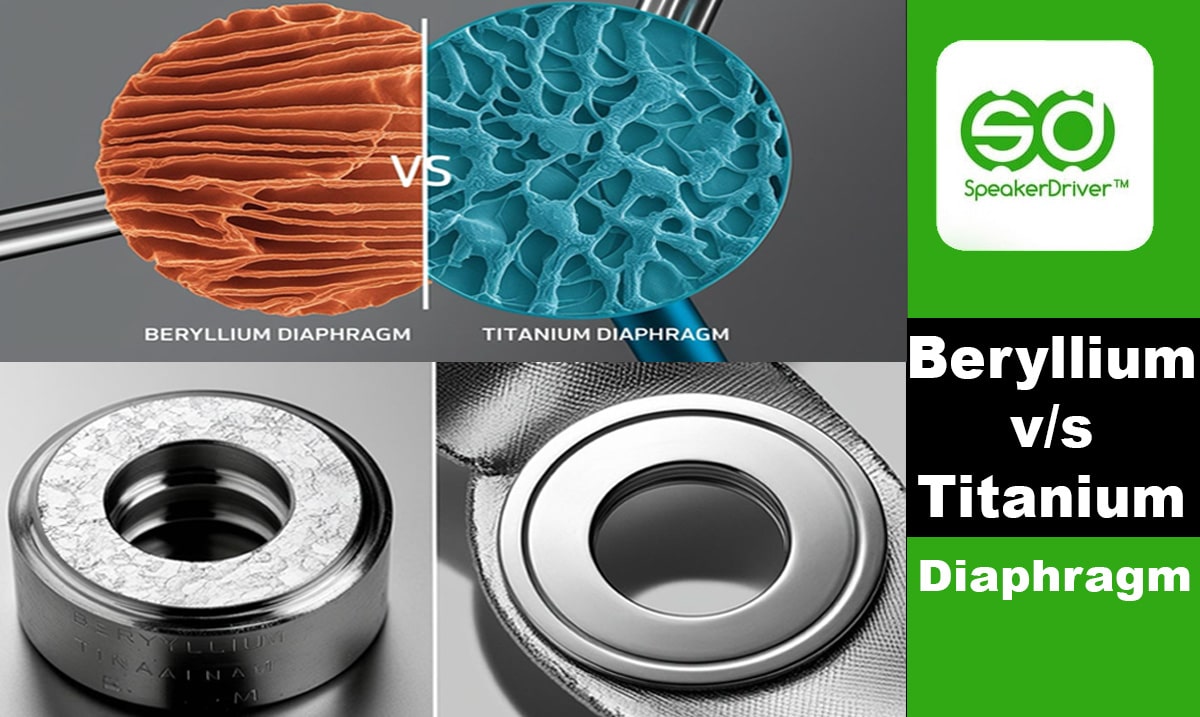
Beryllium Diaphragm vs Titanium Diaphragm
In high-end audio equipment, the diaphragm material used in drivers significantly affects sound quality, clarity, and durability. Beryllium and titanium are two premium choices, each offering unique advantages. Understanding their properties helps audiophiles and manufacturers select the right material for their applications.
Material Characteristics
- Beryllium – Extremely lightweight and rigid, offering fast response and minimal distortion.
- Titanium – Known for its strength and decent stiffness, with slightly more internal damping than beryllium.
Acoustic Performance Comparison
- High-Frequency Extension – Beryllium excels in delivering ultra-clear highs due to its high stiffness-to-weight ratio.
- Warmth and Tone – Titanium produces a warmer, slightly more relaxed sound, often favored for extended listening sessions.
- Transient Response – Beryllium provides faster and more precise transients compared to titanium.
Technical Comparison Table
| Feature | Beryllium Diaphragm | Titanium Diaphragm |
|---|---|---|
| Stiffness | Very High | Moderate to High |
| Weight | Light | Heavier than Beryllium |
| Speed (Transient Response) | Excellent | Good |
| Damping | Low | Moderate |
| Durability | Fragile | Very Durable |
| Cost | Very High | More Affordable |
Common Applications
-
Beryllium Diaphragm Uses
- High-End Headphones – Focal Utopia, TAD Reference series.
- Studio Monitors – Premium tweeters requiring clarity and speed.
- Audiophile Speakers – Systems where detail and transparency are critical.
-
Titanium Diaphragm Uses
- Consumer Headphones – Offers balance of performance and affordability.
- Car Audio Systems – Durable and handles wide temperature ranges.
- Portable Speakers – Durable and lightweight with decent performance.
Beryllium is the surgeon’s scalpel — precise and sharp. Titanium is the craftsman’s tool — reliable and smooth.