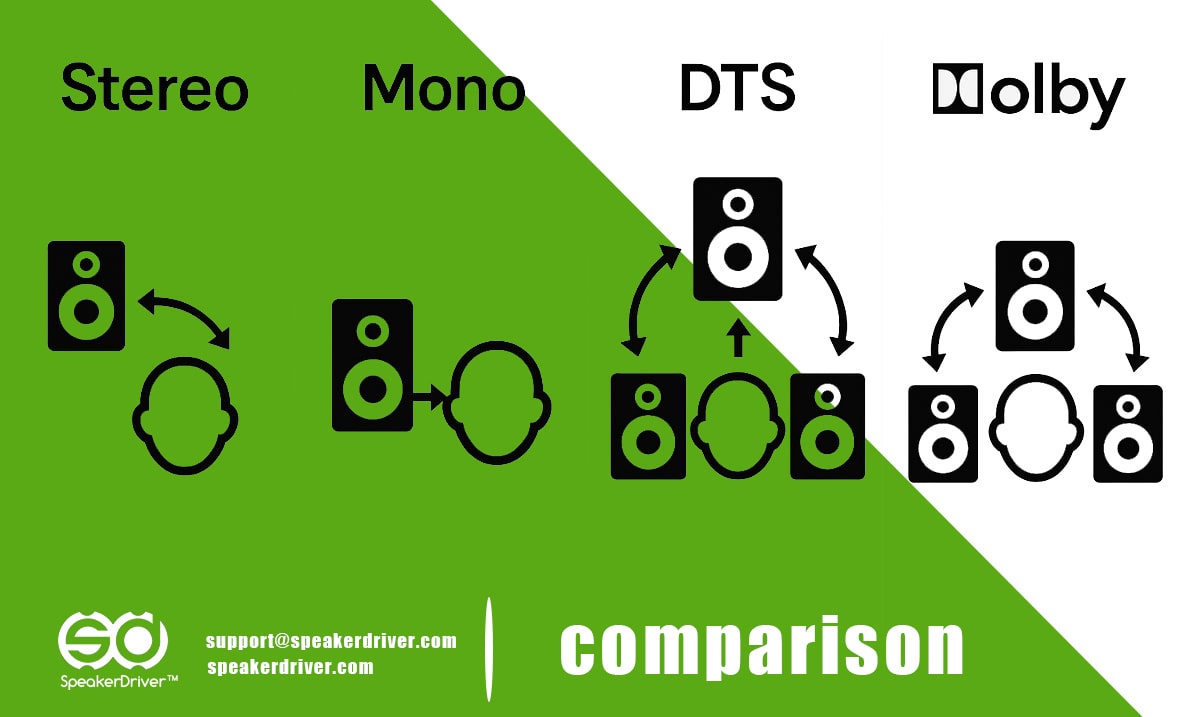
Comparison Guide for Stereo, Mono, DTS, and Dolby
In the world of audio technology, understanding the differences between common audio formats like Mono, Stereo, DTS, and Dolby is essential whether you're an audiophile, filmmaker, content creator, or everyday listener. Each of these audio formats serves different purposes and provides unique auditory experiences. This guide will help you understand what sets them apart and where they are best used.
1. Mono Audio
Mono or monophonic sound uses a single audio channel. Regardless of how many speakers are involved, the same signal is sent to each speaker.
- Use Cases: Phone calls, AM radio, PA systems, voiceovers.
- Advantages: Simple setup, smaller file sizes, consistent sound in all directions.
- Disadvantages: No spatial effects, flat and less immersive experience.
2. Stereo Audio
Stereo uses two distinct audio channels (left and right) to create a sense of direction and space. It is the most widely used format in music and consumer audio.
- Use Cases: Music streaming, headphones, TV, gaming.
- Advantages: Immersive experience, directional sound, greater depth.
- Disadvantages: Requires precise speaker placement; less effective if heard from one side only.
3. DTS (Digital Theater Systems)
DTS is a multi-channel surround sound format developed for home cinema and theatrical use. It uses less compression than Dolby Digital, potentially offering higher fidelity.
- Use Cases: Home theaters, Blu-ray discs, cinemas.
- Advantages: High-quality surround sound, better dynamic range, less compression.
- Disadvantages: Larger file size, requires compatible playback systems.
4. Dolby (Dolby Digital, Dolby Atmos)
Dolby audio technology comes in several formats. Dolby Digital is widely used in DVDs and broadcasts, while Dolby Atmos adds height channels for a 3D audio experience.
- Use Cases: Streaming services (Netflix, Disney+), gaming, theaters, soundbars.
- Advantages: Advanced surround sound, scalable formats (from 5.1 to Atmos), immersive height effects in Atmos.
- Disadvantages: Requires Atmos-compatible hardware and content for full benefits.
5. Comparison Table
| Format | Channels | Sound Quality | Immersion Level | Common Use |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mono | 1 | Basic | Low | Phone calls, radio |
| Stereo | 2 (L/R) | Good | Moderate | Music, TV, games |
| DTS | 5.1/6.1/7.1 | High | High | Home theaters |
| Dolby Atmos | Up to 128 | Very High | Very High | Streaming, cinema, gaming |
Conclusion
Each format serves a specific purpose—mono for simplicity, stereo for basic spatial sound, DTS for cinematic quality, and Dolby for cutting-edge immersive experiences. Choosing the right one depends on the content type, device compatibility, and desired experience.
Quote
"Good sound doesn’t just deliver audio—it transports the listener into the heart of the experience."









