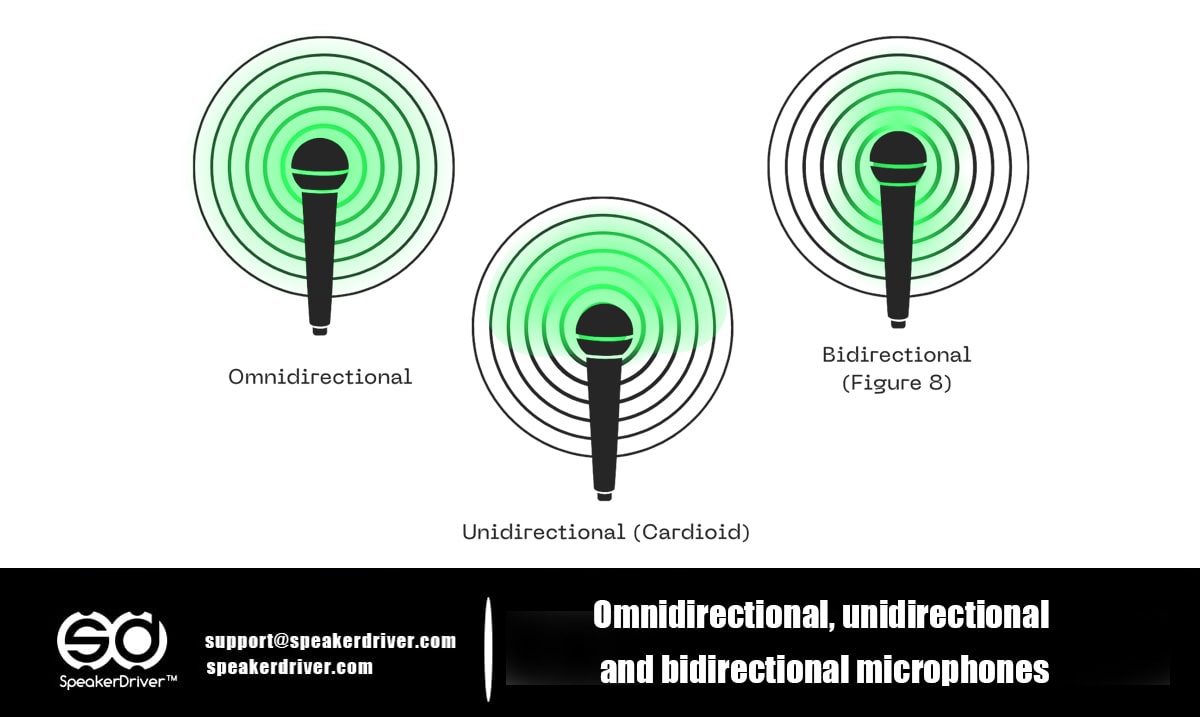
What is the Difference Among Omnidirectional, Unidirectional, and Bidirectional Microphones
Microphones come in various types not only based on their internal components but also on their polar patterns—the way they pick up sound from different directions. The three most commonly discussed microphone polar patterns are omnidirectional, unidirectional, and bidirectional. Understanding these patterns helps you select the right microphone for specific recording or broadcasting needs.
1. Omnidirectional Microphones
Omnidirectional microphones pick up sound equally from all directions—front, back, sides, and top. Their pickup pattern is spherical, making them ideal for capturing natural ambiance.
- Pickup Pattern: 360-degree coverage
- Ideal For: Conference rooms, lavalier mics, capturing room tone
- Advantages: Natural sound capture, no need to point mic directly at the source
- Disadvantages: Prone to background noise and feedback in noisy environments
2. Unidirectional Microphones
Unidirectional microphones are designed to pick up sound primarily from one direction. The most common type is the cardioid microphone, which captures sound from the front while rejecting sound from the sides and rear.
- Pickup Pattern: Heart-shaped (cardioid), also includes supercardioid and hypercardioid types
- Ideal For: Stage performances, vocals, podcasting
- Advantages: Focused sound capture, better isolation, reduced background noise
- Disadvantages: Requires proper positioning, may reject desired ambient sound
3. Bidirectional Microphones
Bidirectional microphones, also known as figure-8 microphones, capture sound from the front and rear while rejecting sounds from the sides. They are commonly used for two-person interviews or for capturing instruments in stereo setups.
- Pickup Pattern: Figure-8 (front and back)
- Ideal For: Duet vocals, face-to-face interviews, stereo room recordings
- Advantages: Natural stereo imaging, front-and-back capture
- Disadvantages: Sensitive to off-axis sounds, prone to feedback if misused
Comparison Table
| Polar Pattern | Directionality | Best Use Cases | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Omnidirectional | All directions | Ambient sound, meetings, group vocals | Natural capture, no aiming needed | Picks up background noise |
| Unidirectional (Cardioid) | Front-focused | Live vocals, podcasting, instruments | Isolates sound, reduces noise | Requires careful positioning |
| Bidirectional | Front and back | Interviews, stereo miking | Captures two sources simultaneously | Rejects side sounds, prone to side noise if misused |
Conclusion
Choosing between omnidirectional, unidirectional, and bidirectional microphones depends largely on your recording environment and what you’re trying to capture. For natural room sounds, go with an omnidirectional mic. For focused audio like vocals or solo instruments, a unidirectional mic is ideal. And for interviews or dual sound sources, a bidirectional mic is your best bet. Understanding these patterns ensures optimal sound quality for your specific application.









